Overview
Static Reactor is specific unit which is designed for the high energy impact on oil-based and other liquids. It uses a cavitation for breaking long molecular chains into a smaller ones and intensifying mixing process.
Functions
Static reactors are designed for improving oil and oil-based products by the decrease of viscosity, flash point and pour point.
Being a very effective unit for the mixing it amplifies an impact of additives which are normally used for improving the quality of oil, Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO, mazut) and other products.
Another function of static reactor is an improved mixing process of liquids and gases. For example, ozone is added to a water or other liquid is well mixed with with bubbles size below micrometers.
Oil, passed through the static reactor, has higher output of light fractions like benzin and diesel. Oil and oil-based fuels becoming uniform what improves combustion characteristics.
Applications
Static reactors are effective for improving Heavy Fuels Oils (HFO), mazut, oil wastes, etc. Watered oil is becoming homogeneous (uniform). Major applications are:
- In oil-refineries – for increasing light oil fractions output, reducing consumption of catalysts, dissolving liquid and gazeous additives, etc.
- In combustion systems – for improving combustion characteristics, reducing sledging, etc.
- Special applications – dissolving liquid additives and gases in oil, micromilling of solid particles which may exist in oil, especially in heavy fuel oil, other applications.
Depending on oil characteristics static reactor may reduce oil viscosity up to 30%, reduces pour point from -6 deg C till -16 deg C, increases output of light fractions on 2…3% or more for different types of oil. Watered oil processed in DEWA-OIL becomes uniform and does not include “water lenes”, produced water-oil emulsion is stable for a long period.
How it Works
Oil is pumped with a certain pressure into the Static Reactor which produces a myriads of bubbles (caverns). These caverns are collapsing immediately after they are produced. This process (cavitation) creates a local pressure inside a bubble up to hundreds bars (locally) and destructs long molecular chains. As the result all components (oil, water, additives, ..) are properly mixed in a form of stable emulsion.
Multi-stage turbulent sections are designed inside the reactor in order to create conditions for the cavitation. Due to media viscosity&density are different, static reactors for non-standard liquids are designed individually.
Normal working pressure for static reactor is 12…20 bars depending on oil or other media type.

Effects & Results
Static Reactor makes a remarkable own impact on oil (FO, HFO) pour point, viscosity and flash point. Based on results of our customers static reactor amplifies an impact of catalysts significantly reduces its’ total consumption.
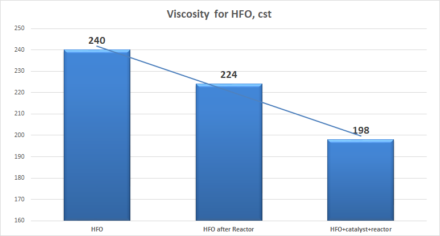
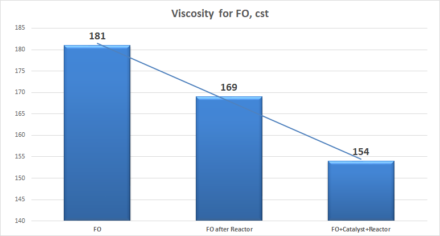
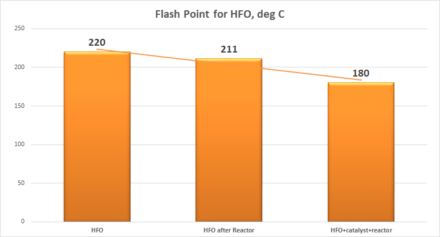
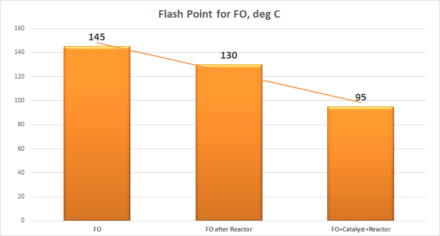
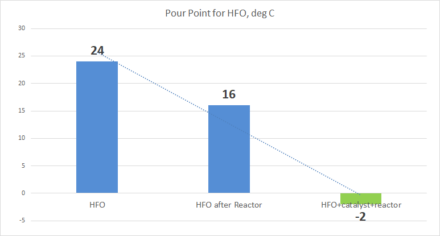
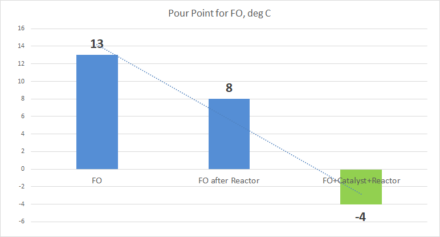
Results of processing HFO and FO in a static reactor with and without catalyst show change in parameters up to 30%:
| Flash Point | Pour Point | Viscosity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FO | 145 | 13 | 181 |
| FO after Reactor | 130 | 8 | 169 |
| FO+Catalyst+Reactor | 95 | -4 | 154 |
| HFO | 220 | 24 | 240 |
| HFO after Reactor | 211 | 16 | 224 |
| HFO+catalyst+reactor | 180 | -2 | 198 |